- Home Page
- Company Profile
-
Our Products
- Aluminium Castings Products
- Aluminum Sand Castings
- Aluminium Bronze
- Leak Proof Casting
- Bronze Casting
- Aluminum Castings
- Aluminium Bronze Castings
- Aluminium send Castings
- Manganese Bronze
- Impeller Bronze Casting
- Power Distribution Casting
- Non Ferrous Castings
- Sand Casting
- Aluminium Sand Casting
- Intake Manifold Aluminum Sand Castings
- Defence Aluminium Sand Casting
- Tap Changer Aluminium Sand Casting
- Gear HSG Aluminium Sand Casting
- Aluminium Sand Casting
- Heat Exchanger Aluminium Sand Casting
- Aluminium Pump Sand Casting
- Power Transmission Aluminium Sand Casting
- Aluminum Gravity Die Castings
- Copper Based Alloys Castings
- Aluminum Moulds Castings
- Wooden Patterns Castings
- Metalic Patterns Castings
- Contact Us

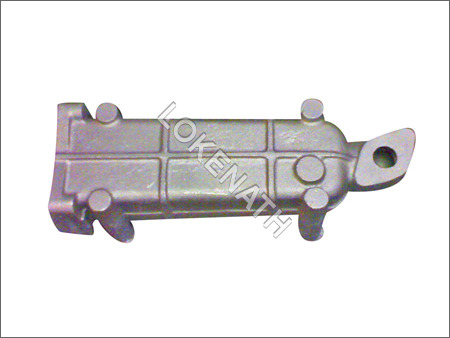
Die Casting
450 INR/Piece
Product Details:
X
Die Casting Price And Quantity
- 1 Unit
- 450 INR/Piece
Die Casting Trade Information
- Cheque
- Per Day
- Days
- Yes
- Asia
- All India
Product Description
With our profound experience of the relative market, we are able to establish ourselves as an important manufacturer, supplier and exporter of premium quality Thin Walled Die Casting. These casting are highly demanded in the market due to their accurate dimensions and corrosion resistance. Widely used in various engineering industries, this range of Thin Walled Die Casting is available in various sizes and specifications as per the specific requirements of our customers.
Features
- High resilience
- Longer life
- Leak proof
- Die Preparation: A permanent mold, or die, is created from high-strength steel into two or more sections.
- Clamping: The die sections are clamped tightly together on a die-casting machine.
- Injection: Molten metal is injected into the die cavity under high pressure and at high speed.
- Solidification: The molten metal cools and solidifies rapidly within the die.
- Ejection: The die opens, and the finished casting is ejected from the mold.
- Finishing: The part is removed and may undergo trimming or other post-processing steps.
- High Precision: Produces parts with excellent dimensional accuracy.
- Complex Shapes: Can form intricate geometries and complex parts.
- Smooth Finish: Results in a smooth surface finish, reducing the need for post-processing.
- High Production Volume: Ideal for mass production due to fast cycle times and repeatable results.
- Cost-Effective: Low cost per part for large production runs.
Die casting is a mass-production manufacturing process where molten metal is forced into a reusable metal mold, called a die, under high pressure. This method creates high-quality, dimensionally accurate metal parts, often with intricate shapes, from materials like aluminum, magnesium, and zinc alloys. The die is typically made of steel and opens to eject the solidified part, which then undergoes minimal finishing before use.
The Process
The die casting process involves several key steps:
Key Characteristics & Benefits
Materials Used
Die casting primarily uses non-ferrous metals and their alloys, including: aluminum, magnesium, zinc, and copper.
Applications
The process is widely used for manufacturing automotive components, appliance parts, toys, and other products requiring high precision and complex shapes.
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email